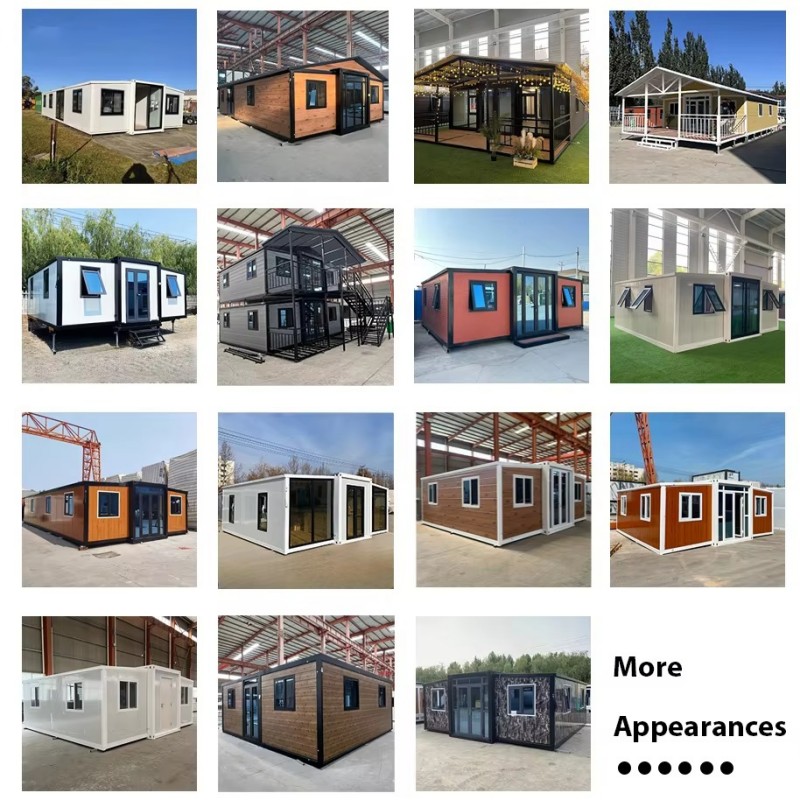
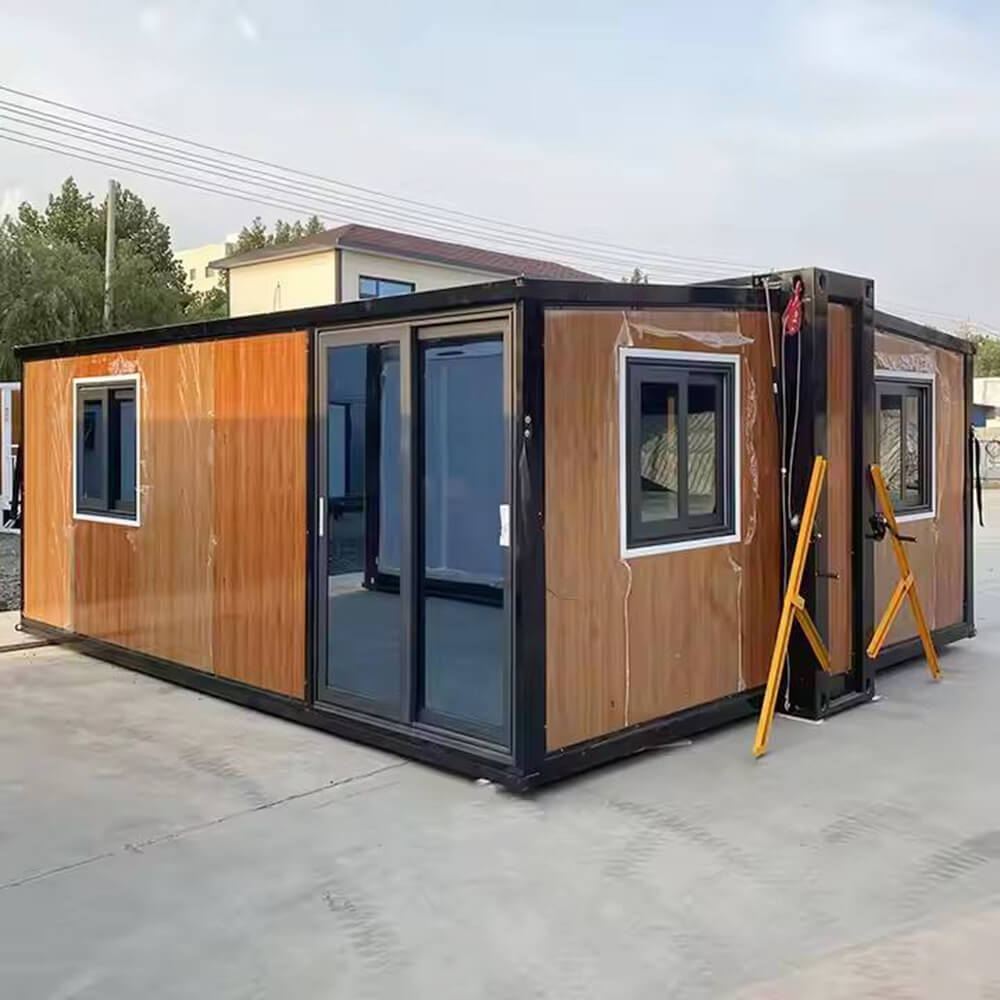
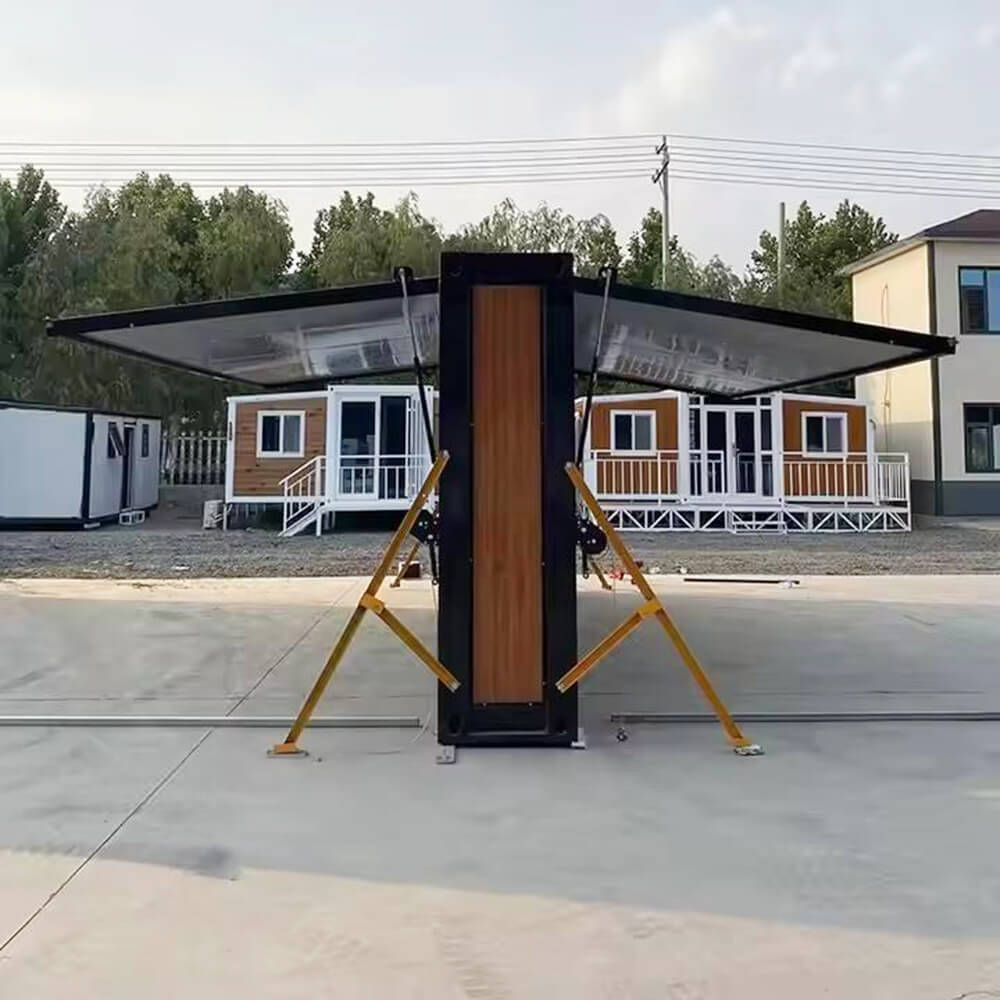
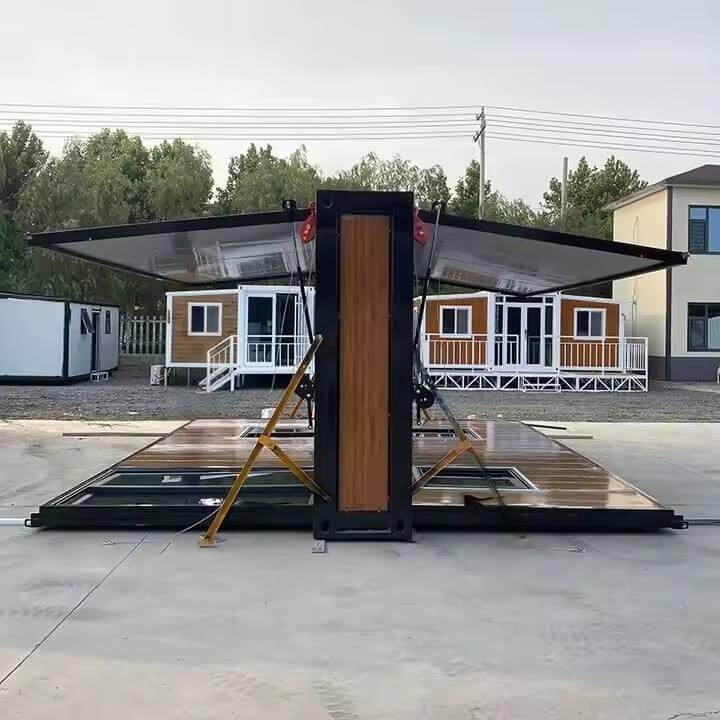
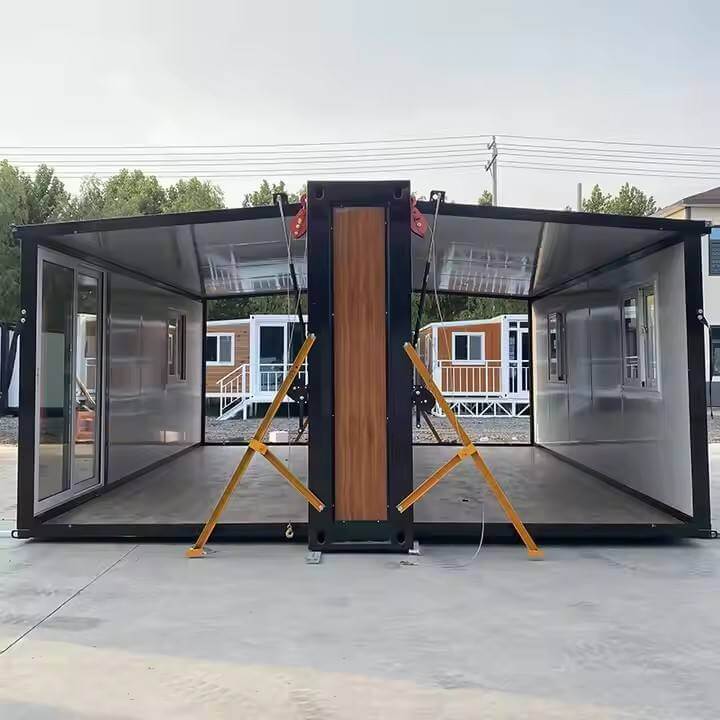
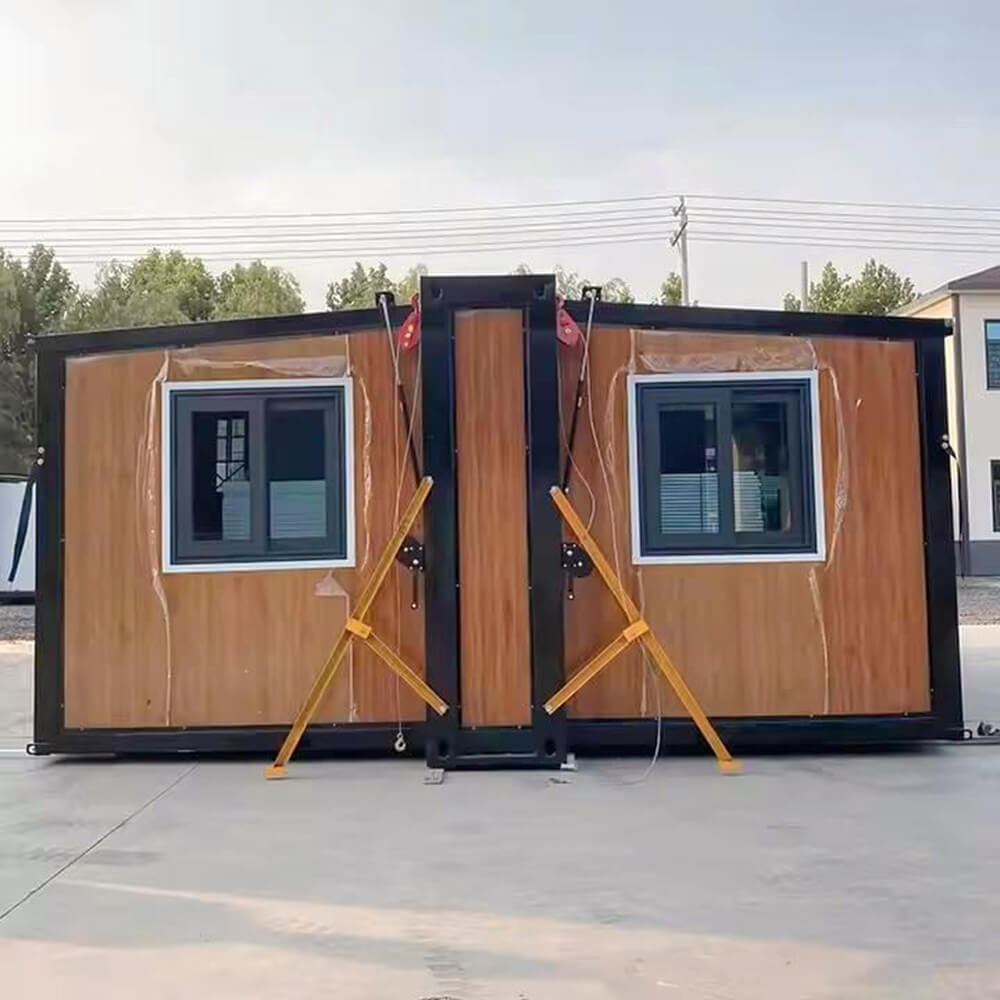
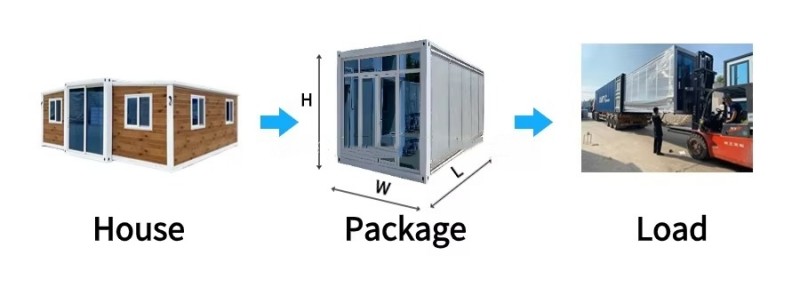
Modular Expansion Design:
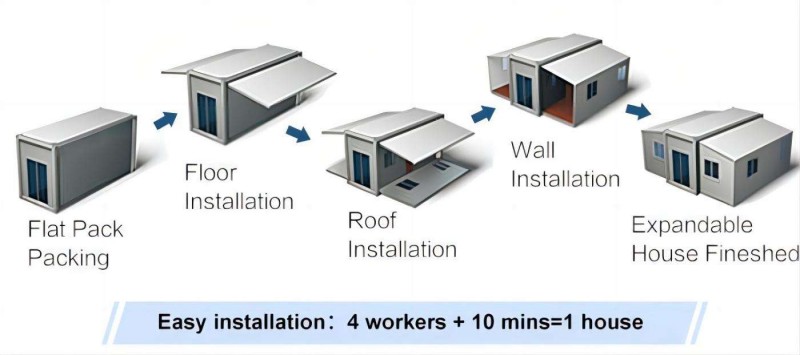
Utilizes an expandable container module structure that compresses during transport. On-site assembly enables rapid deployment and flexible adaptation to diverse sites by expanding usable space.
Wood-Like Exterior Finish:
Exterior walls feature wood-imitation materials for a natural, aesthetically pleasing appearance. Seamlessly integrates into rural or scenic environments, enhancing visual appeal and contextual harmony.
Large Glass Door Lighting Advantage:
Large sliding glass doors significantly enhance natural indoor lighting, creating an open and airy space while facilitating easy access and visual interaction between indoors and outdoors.
Multi-Window Ventilation Design:
Multiple strategically placed windows ensure air circulation, improve indoor air quality, and enhance comfort during use.
Prefabricated Integrated Production:
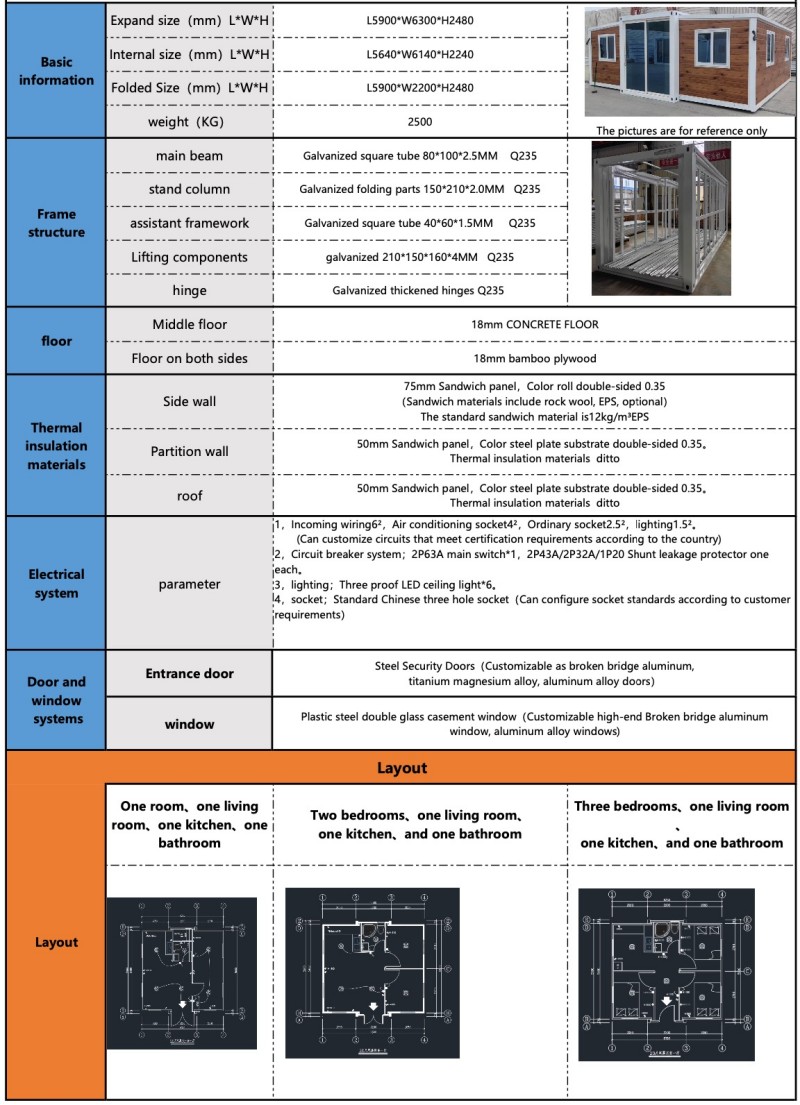
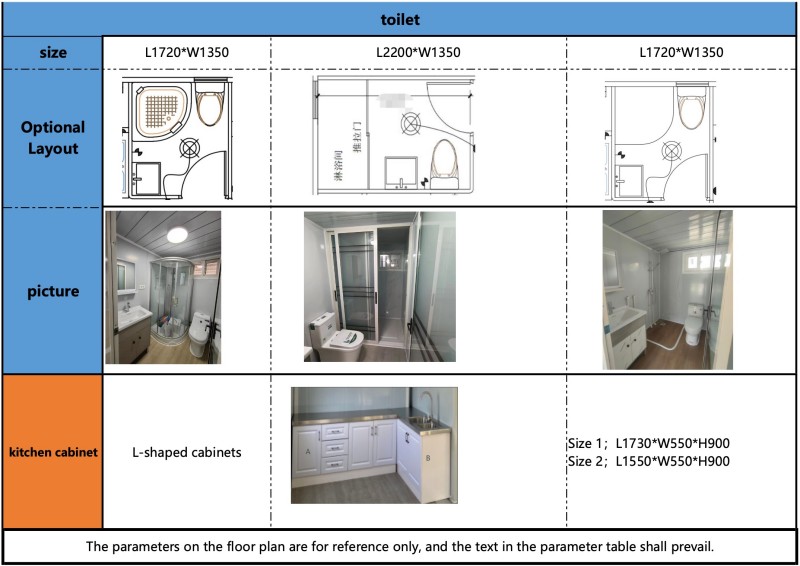
Basic systems like plumbing, electrical, and insulation are integrated during factory prefabrication. Minimal on-site construction is required upon arrival, enabling rapid deployment and saving construction time.
Temporary Living Space Applications:
Serves as temporary accommodation such as construction site dormitories or guest rooms for homestays, providing convenient rest areas for occupants.
Mobile Office Functionality:
Ideal as temporary workspaces for outdoor exhibitions or mobile offices for small startups, meeting flexible work requirements.
Tourist Attraction Service Platform:
Can be adapted into ticket booths, visitor service centers, or small retail shops within scenic areas, supporting tourism infrastructure development.
Emergency Disaster Relief Function:
Rapidly transportable to disaster zones for use as temporary shelters, providing affected populations with immediate refuge and basic living space.
Reusable Design:
Features a robust, modular structure that can be disassembled, relocated, and reassembled at new sites as needed, ensuring excellent reusability and reducing long-term costs.
How effective is the insulation in this container home?
The thermal insulation performance of container houses primarily depends on material selection, structural design, and manufacturing processes. Based on the common characteristics of such modular structures, the analysis is as follows:
1. Insulation Materials and Structure
Standard products typically employ composite insulation panels (e.g., polyurethane sandwich panels, rock wool sandwich panels). The insulating core layer within these panels (generally 50–100mm thick) effectively blocks heat transfer. Its low thermal conductivity minimizes temperature exchange between interior and exterior environments.
2. Door and Window Sealing
The configuration includes large glass doors and multiple windows. Using high-performance sealing profiles (e.g., thermal break aluminum) combined with double-pane insulated glass minimizes heat loss through gaps. However, subpar sealing techniques may compromise insulation effectiveness (depending on the manufacturer’s configuration standards).
3. Applicable Scenarios and Limitations
In temperate/subtropical regions, combined with insulation panels and effective sealing, it can naturally maintain comfortable temperatures in spring and autumn. With supplemental air conditioning/heating in winter and summer, it achieves significant energy savings.
In extremely cold/hot regions, verify if the manufacturer has reinforced insulation for roofs and floors (some premium products feature enhanced whole-house insulation systems). Lower-end configurations may require additional insulation measures.
4. Impact of Manufacturer Variations
Reputable brands strictly control insulation thickness, density, and flame retardancy, ensuring more consistent thermal performance. Small workshops may cut corners on insulation layers, compromising effectiveness.
In summary, properly manufactured container homes provide adequate insulation for temporary structures or auxiliary living spaces. Actual performance depends on manufacturer specifications and regional climate conditions.